Onchocerciasis
What Is Onchocerciasis?
Onchocerciasis, also known as river blindness and Robles disease, is a neglected tropical disease (NTD) caused by infection with the parasitic worm Onchocerca volvulus.
Onchocerciasis is an eye and skin disease caused by a worm (filaria) known scientifically as Onchocerca volvulus. It is transmitted to humans through the bite of a blackfly (simulium species).
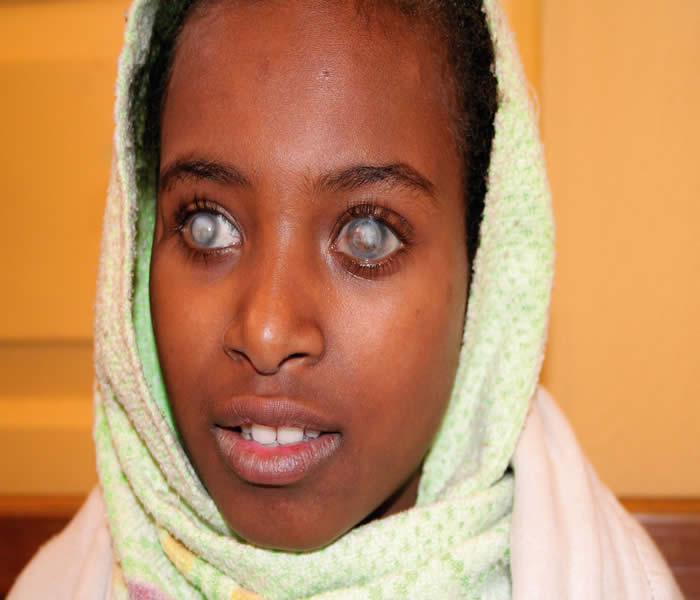
What Is Trachoma?
Note: Trachoma is the leading infectious cause of blindness in the world today.
Trachoma a contagious bacterial infection of the eye in which there is inflamed granulation on the inner surface of the lids
Trachoma is an infection of the eyes that may result in blindness after repeated re-infections, it also known as granular conjunctivitis, Blinding trachoma and Egyptian ophthalmia. It is an infectious disease caused by bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis.
The infection causes a roughening of the inner surface of the eyelids. This roughening can lead to pain in the eyes, breakdown of the outer surface or cornea of the eyes, and possibly blindness as the name implies.
As the infection progresses, it causes eye pain and blurred vision. If the infection is untreated, scarring occurs inside the eyelid. This leads to the eyelashes turning inward toward the eye, a condition called trichiasis.
Trachoma is contagious, spreading through contact with the eyes,
Trachoma spreads easily from person to person and it can pass from child to child and from mother to child within the family.
Causes of Trachoma
Trachoma is an infectious eye disease caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis, which spreads by contact with an infected person’s hands or clothing.
WHO’s report:
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), trachoma is responsible for the visual impairment of 2.2 million people, of whom 1.2 million are irreversibly blind.
Symptoms/Signs of Trachoma
Signs and symptoms of trachoma usually affect both eyes and may include:
- Cloudy cornea
- Discharge from the eye
- Eye pain
- Eyelid swelling
- Itching and irritation of the eyes and eyelids
- Photophobia
- Swelling of lymph nodes just in front of the ears
- Turned-in eyelashes
Other symptoms are:
After repeated infections, when scarring of the conjunctiva has occurred, the patient may complain about a feeling of sand or insects in the eyes. Individual may complain about sticky eyes or itchy, painful eyes.
How to diagnose Trachoma
The diagnosis of trachoma is done clinically.Although there are bacteriologic and other tests available, It can also be diagnosed by examining the eyes and eyelids of the patient. In developed countries though very rear, the diagnosis is usually by the ophthalmologist. Often the disease is subclinical.
Clinically the diagnosis of trachoma can be done by using magnifiers (loupe) and a flashlight.
Trachoma should be suspected from the history and symptoms. It then can be confirmed by an examination which can be performed within the community without the aid of sophisticated office equipment.
If equipment is available, the vision is measured and the eye is inspected with a slit lamp (biomicroscope), with which characteristic changes in the lids, tear film, conjunctiva, and cornea can more easily be seen.
How to Prevent Trachoma
If you've been treated for trachoma with antibiotics or surgery, reinfection is always a concern. For your For you to prevent and safe you and others,Go for with your family members for trachoma screening and if necessary, treat trachoma.
When in regions where trachoma is common like Africa and some part of Europe, take extra care in practicing good hygiene, which can help prevent infection.
Proper hygiene practices include:
- Controlling flies: Reducing fly populations can help eliminate a major source of transmission
- Face washing and hand-washing. Keeping faces clean may help break the cycle of reinfection
- Improved access to water: Having a fresh water source nearby can help improve hygienic conditions
- Proper waste management: Properly disposing of animal and human waste can reduce breeding grounds for flies
Note: No trachoma vaccine is available, but prevention is possible. The World Health Organization (WHO) has developed a strategy to prevent trachoma, with the goal of eliminating it by 2020.
The strategy, titled SAFE, this could be found under treatment.
Treatment for Trachoma
Treatment consists of antibiotics or simple surgery.
The World Health Organization (WHO) developed the SAFE strategy.
S = surgical care
A = antibiotics
F = facial cleanliness
E = environmental improvement
Surgery = to prevent blindness by eyelid surgery to correct inverted eyelashes
Antibiotics= community wide distribution of antibiotics to treat active infection
Face washing = to stop eye-seeking flies that spread infection
Environment= to give communities access to water and improved sanitation
Trachoma Home Remedies/Home Cure
Eyebright herb is one of the best natural home remedies for Eye Infections. You can take eyebright tea, tincture or liquid extract, or use a light mixture (a teaspoon of dried eyebright steeped in a pint of boiling water) as an eye wash about 3-4 times in a day. It can also be used as a compress over eyes.
Complications of Trachoma
- Corneal scarring or cloudiness
- Eyelid deformities, such as an inward folding eyelid (entropion) or ingrown eyelashes (trichiasis)
- Partial or complete vision loss
- Scarring of the inner eyelid
- Untreated, repeated trachoma infections can result in a form of permanent blindness when the eyelids turn inward




