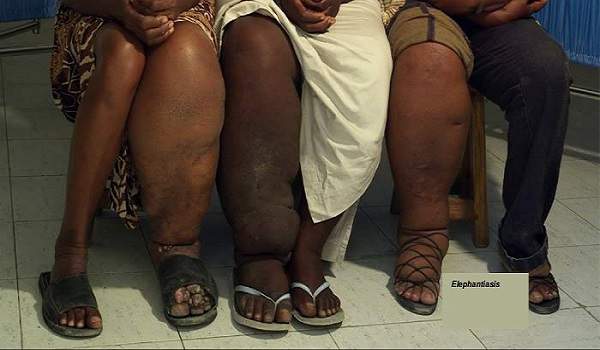
Elephantiasis
What is Elephantiasis?
Elephantiasis refers to a parasitic infection that causes extreme swelling in the arms and legs. The disease is caused by the filarial worm, which is transmitted from human to human via the female mosquito when it takes a blood meal. Elephantiasis is a syndrome caused by infection with a nematode parasite called the filarial worm.The parasite grows into an adult worm that lives in the lymphatic system of humans. It is transmitted by female mosquitoes.
When an infected female mosquito bites a person, she may inject the worm larvae into the bloodstream. The worm larvae reproduce and spread throughout the bloodstream, where they can live for many years.
Elephantiasis is caused by several different types of parasitic worms, including Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi, and B. timori.
Causes of Elephantiasis
Nematode parasites that causes lymphatic filariasis includes Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi, and Brugia timori. The larvae (microfilariae) of the parasite are taken up by the mosquito when it feeds. When the larvae reach the third stage of development, they are introduced to a new host, who then develops the infection.
Symptoms/Signs of Elephantiasis
In many cases, symptoms of elephantiasis do not appear until years after infection. As the parasites accumulate in the blood vessels, they can restrict circulation and cause fluid to build up in surrounding tissues. The symptoms may include:
- Blocked lymph ducts
- Brawny skin color
- Enlarged groin lymph nodes
- Fever
- Fibrotic skin tissue
- Impaired lymphatic drainage
- Massive leg swelling
- Pain in testicles
- Pain above testicles
- Pebbly skin appearance
- Severe swelling
- Skin ulceration
- Thickened skin tissue
- Verrucous skin appearance
How to diagnose Elephantiasis
Microfilariae sometimes can be seen in blood under a microscope. Often the doctor diagnoses the disorder based on the symptoms and a medical history, after ruling out other disorders with similar symptoms.
How to Prevent Elephantiasis
Apply ointment: Applying ointment will act almost like a shield against the microfilariae. Even after you are infected, applying ointment will cleanse the lymph nodes and skin, resulting in faster results.
Compressive bandages: Using compressive bandages manages to secrete the lymphatic juice, whereas before, the flow was blocked, causing the swelling.
Giving antibiotics to prevent infection:
Surgically removing infected tissue:
Use bug spray: Again the main goal is to keep away mosquitoes. Using bug spray will ward off any unwanted vectors such as mosquitoes.
Spraying to kill mosquitoes:
Wear clothes with lots of coverage: Wearing clothes with lots of coverage will help protect you from mosquito bites. Just like any other mosquito precaution, it will limit the skin exposed, therefore, decreasing the chances of being bitten.
Wear shoes: This will cover up your feet, and keep the mosquitoes and other chemicals away from them.
Wash hands, feet, and body: This will keep your body clean, and help prevent serious infection. If you are infected, and your skin is cleansed, it will do less damage.
Whereas if your skin is dirty, then those chemicals and dirt particles also enlarge the organs

Management of symptoms
Relatively simple and well known surgical procedures are available to correct hydrocele. Because secondary bacterial infections play an important role in precipitating acute adenolymphangitis episodes and progression of lymphoedema, simple hygiene measures – either alone or in combination with antibiotic treatment – play an important role in preventing episodes of acute disease and in the management of lymphoedema. Daily washing of affected limbs with soap and safe water to prevent secondary infection, combined with simple exercises, elevation of the limb, and treatment of cracks and entry points, provides significant relief from acute episodes and slows progression of the disease.
Treatment for Elephantiasis
The main medication used to treat this condition is diethylcarbamazine or DEC, which kills the microfilariae as well as some adult worms. The medication is usually well tolerated but side effects include dizziness, fever and aching muscles. Though most times medications are not very effective against adult worms. New microfilariae produced by the adult worms often continue to show up months after treatment.
Elephantiasis Home Remedies/Home Cure
- Carefully wash the swollen area with soap and water every day
- Disinfect wounds if any using antibacterial and antifungal creams
- Elevate and exercise the swollen arm or leg to improve the lymph flow
- Maintain proper hygienic conditions
- Use insect repellants and mosquito nets
Elephantiasis can complicate itself to very dangerous levels if left untreated in the early stages. The following are some of the drastic complications that can occur in men:-
Hydrocele is very commonly observed in men who suffer from elephantiasis. Hydrocele is the accumulation of fluids in the testicles. This is a very painful condition, which renders men impotent.
Similarly, elephantiasis of the penis and the scrotum in males is a very painful condition and can lead to impotency.
In women, the elephantiasis can spread to the vulva. This could make it impossible for the woman to enjoy penetrative sex and to conceive.
This causes tumerous growths, which may make the condition quite severe.
Elephantiasis can cause damage to the lungs in the form of eosinophilia, in which there is an increase in the number of eosinophils in the blood. This condition is characterized by a wheezing cough and fevers.
Prolonged elephantiasis can cause failure of the kidneys.




