Boils and Abscesses
What Is Boils and Abscesses?
Hives (or urticaria) are red raised bumps or welts on the skin. They can appear anywhere on the body and can look like tiny little spots or large interconnected bumps. Individual hives can last anywhere from a few hours to a week (sometimes longer), and new ones might replace those that fade.
It can be triggered by many substances or situations and usually starts as an itchy patch of skin that turns into swollen red welts.
What Is Boils and Abscesses?
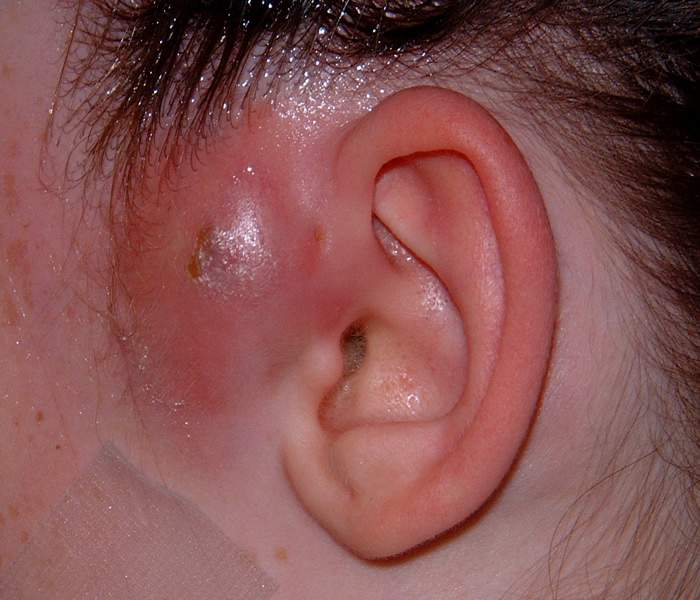
A boil, or skin abscess, is a collection of pus that forms in the skin. The pus may be yellow or green and may have a bad smell.
It is a localized collection of pus that generally develops in response to infection or to the presence of other foreign materials under the skin. A boil is typically painful, and it appears as a swollen area that is tender warm to the touch. The skin surrounding an abscess often appears pink or red. Abscesses can develop in many parts of the body, but they usually involve the skin surface.
Abscesses and Furuncle are other words for a boil. Boils are bacterial or fungal infections of hair follicles. The infected hair follicle can be on any part of your body, not only your scalp. When the hair follicle becomes infected, the skin around it becomes inflamed
Causes of Boils and Abscesses
The usual cause of an abscess is an infection with bacteria.
When foreign organisms such as bacteria enter the body, the immune system sends white blood cells to fight the infection. This causes swelling (inflammation) at the site of infection and the death of nearby tissue, creating a hole called a cavity, which fills with pus to form an abscess. It also includes:
- Poor hygiene
- Poor immune system
- Alcoholism
- Friction from tight clothing
- Diabetes
- Poor nutrition
- Chemotherapy
- Exposure to harsh chemicals
Boils and Absence can be on any part of your body, especially on:
- Buttocks
- Genitals
- Hands and feet
- Trunk
- Underarms
Symptoms/Signs of Boils and Abscesses
A boil starts as a hard, red, painful lump usually less than an inch in size. Over the next few days, the lump becomes softer, larger, and more painful. Soon a pocket of pus forms on the top of the boil. Signs of a severe infection are:
- Boil develops with a red nodule or head on any part of the body.
- Boil gets bigger with the passage of time.
- It gets filled with pus, which gives it whitish appearance.
- Around the boil, skin becomes hard and painful.
- Sometimes, boils are very itchy.
- Boil can appear either single or collectively on the skin.
- Lymph gets swelled during the development of a boil.
If you have a skin abscess, your doctor will examine the affected area, ask how long you've had the abscess, whether you've injured that area and whether you have any other symptoms.
A sample of pus may be taken from your abscess and sent for testing. This allows the specific bacteria causing the abscess to be identified, which can help determine the best way of treating it.
If you've had more than one skin abscess, you may be asked to give a urine sample. This will be tested for glucose, which is a sign of diabetes.
How to Prevent Boils and Abscesses
It is more common in people who smoke or are obese so
Stop smoking
Losing weight may help to prevent boils. It is also more common in young people (aged less than 30), people with diabetes and people who have taken an antibiotic in the previous six months. Some people seem to be particularly prone to developing boils. The boils can develop continuously, or occur from time to time.
Treatment for Boils and Abscesses
- If the boil is large, your doctor may need to open it up and drain the pus. This is done with a scalpel after the area of the boil is numbed with a local anesthetic.
- If the infection is deep, your doctor may put some gauze in the incision to keep it open and draining. The gauze is usually removed in two days.
- If there are concerns about the seriousness of the infection, blood tests may be needed. The doctor may prescribe antibiotics if the infection is severe.
- A large skin abscess caused by a staph infection may need to be surgically opened and drained and treated with intravenous antibiotics.
If the boil causes swollen nodes or fever, take penicillin tablets orerythromycin or dicloxacillin, take 500 mg by mouth, 4 times a day for 7 days.
Boils and Abscesses Home Remedies/Home Cure
Epsom Salt
Epsom salt is an astringent, which can draw out the pus and associated impurities from your boil. Its antibacterial properties protect the area from secondary infections as well. There are a couple of ways you can use Epsom salt to treat your boils: You can add ¼ cup of Epsom salt in two cups of warm water and use it as a warm compress.
You can add a cup of Epsom salt into your bathwater and take a twenty minute bath. You can take this bath up to three times a day. Do not over-indulge in this treatment as it may leave your skin feeling dry.
Egg Whites
There is a lot of anecdotal evidence that suggests that egg whites can be a highly effective treatment for boils. This is because egg whites are rich in Vitamins A and E, which as mentioned earlier boosts immunity and protects the epidermis.
Simply boil an egg, separate it from the yolk and hold it on the boil using gauze and medical tapes. Replace the dressing every six hours. Eating egg whites will also fortify your system against boils from the inside!
Onions
Onions have natural antiseptic properties that can be used to treat boils. There are a few ways you can apply this treatment:
Simply cut the onion into thick slices, apply a slice on the boil and hold it in place using gauze and medical tapes. Change the dressing every couple of hours.
There is some anecdotal evidence that suggests that grating an onion using a food processor and applying the paste as a dressing makes the treatment even more effective.
Boil three regular sized onions in a pan of water. Wait till only 1/3 of the water is remaining. Strain and let the water cool down to room temperature. Wash the boil repeatedly with the water during the course of the day.
Complications of Boils and Abscesses
Cavernous sinus thrombosis
Cavernous sinus thrombosis is a very rare but potentially life threatening complication of a boil. It occurs when an infection triggers a blood clot in the spaces behind the eye socket. The clot begins to increase the pressure on the brain, causing symptoms such as:
- A sharp and severe headache
- Eye pain that's often severe
- Swelling of the eyes
Many new abscesses may form on the joints or other locations on the skin. Skin tissue may die as a result of the infection, leading to gangrene and possible skin loss or amputation. As the infection makes its way through the body internally, it can lead to a condition called endocarditis an inflammation of the inside lining of the heart.
Endocarditis can be fatal if not treated early, and many people will require long-term antibiotic therapy and hospitalization to treat the condition.




