Ear Infections
What is a Middle Ear Infection?
Ear is one of the most delicate sense organs. If it is not cared properly, it may cause several problems, including ear infection. Ear infection is a very common problem, diagnosed in infants and children. Even it is common in adults, now-a-days. The general term used for ear infection is “Otitis Media” or chronic ear infection. Very few people know about the symptoms, causes, and treatment of an ear infection. If we suffer with an ear pain, we always try to sort out a quick remedy to overcome it. Before going through the series of home remedies, let us understand the symptoms and causes of an ear infection.
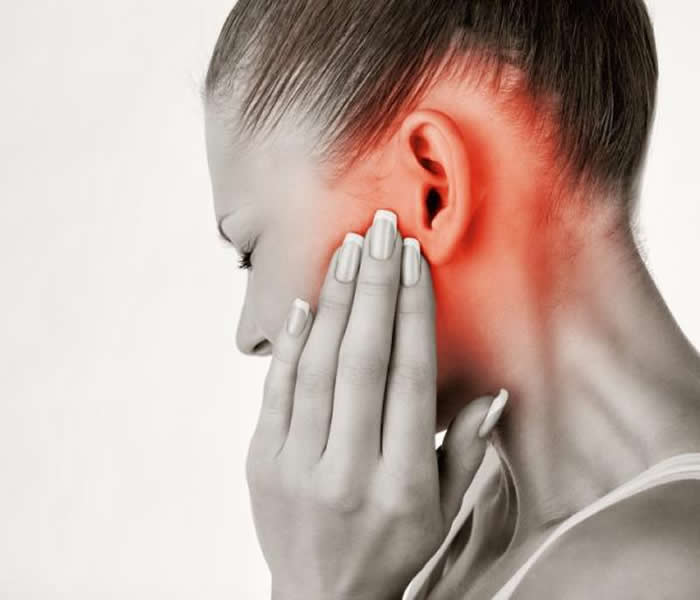
Ear Infections
The ear is divided into three:
- Outer Ear
- Middle Ear
- Inner Ear
When the germs bother your middle ear, it is called ear infection.
What is a Middle Ear Infection?
Ear is one of the most delicate sense organs. If it is not cared properly, it may cause several problems, including ear infection. Ear infection is a very common problem, diagnosed in infants and children. Even it is common in adults, now-a-days. The general term used for ear infection is “Otitis Media” or chronic ear infection. Very few people know about the symptoms, causes, and treatment of an ear infection. If we suffer with an ear pain, we always try to sort out a quick remedy to overcome it. Before going through the series of home remedies, let us understand the symptoms and causes of an ear infection.
Middle ear infections are one of the most common childhood problems, an ear infection occurs when a bacterial or viral infection affects the middle ear—the sections of your ear just behind the eardrum. Ear infections can be painful because of inflammation and fluid buildup in the middle ear. Ear infections can be chronic or acute. Acute ear infections are painful but short in duration.
Acute otitis media (AOM) is the most common ear infection. Parts of the middle ear are infected and swollen and fluid is trapped behind the eardrum. This causes pain in the ear—commonly called an earache. Your child might also have a fever.
Causes of Middle Ear Infections
Most middle ear infections occur when an infection such as a cold, leads to a build-up of mucus in the middle ear and causes the Eustachian tube (a thin tube that runs from the middle ear to the back of the nose) to become swollen or blocked. This mean mucus can't drain away properly, making it easier for an infection to spread into the middle ear.
An enlarged adenoid (soft tissue at the back of the throat) can also block the Eustachian tube. The adenoid can be removed if it causes persistent or frequent ear infections.
Risk Factors
Children/Adult may be at higher risk for ear infections if they:
- Are around people who smoke
- Are male
- Are bottle-fed rather than breast-
- Attend day care (because they are exposed to more germs and viruses).
- Have had previous ear infections.
- Have a family history of ear infections.
- Have nasal speech (caused by large adenoids that block the eustachian tube).
- Have allergies with nasal congestion.
- Have frequent colds or other infections.
- Take a bottle to bed.
- Use a pacifier
- Were born prematurely or with a low birth weight.
Symptoms/Signs of Ear Infections
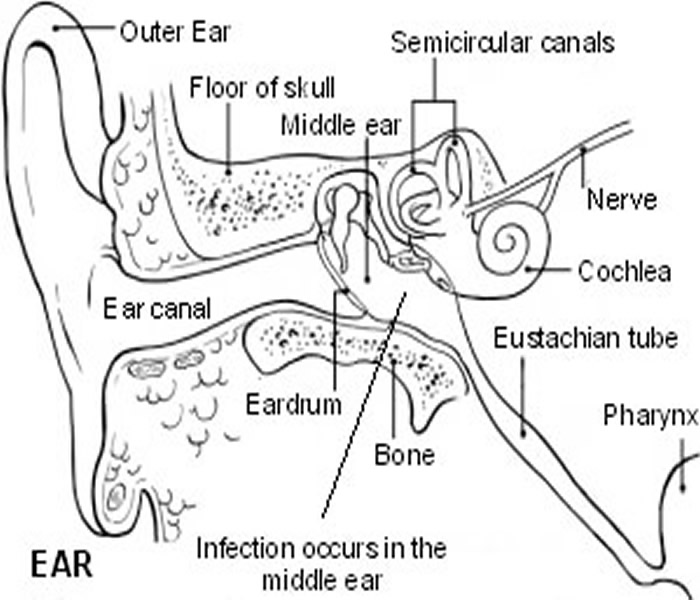
The signs and symptoms of ear infection in Children include:
- Acting more irritable than usual
- Crying more than usual
- Difficulty hearing or responding to sounds
- Difficulty sleeping
- Drainage of fluid from the ear
- Ear pain, especially when lying down
- Fever of 100 F (38 C) or higher
- Headache
- Loss of balance
- Loss of appetite
- Tugging or pulling at an ear
Common signs and symptoms in Adults include:
- Diminished hearing
- Drainage of fluid from the ear
- Ear pain
How to diagnose Ear Infections
It is important to get an accurate diagnosis and prompt treatment when you notice these signs or if the symptoms last for more than a day in your child on in case of aldult consult your doctor. Anyone can develop a middle ear infection but infants between six and 15 months old are most commonly affected.
Diagnosis: Your doctor can usually diagnose an ear infection or another condition based on the symptoms you describe and an exam. The doctor will likely use a lighted instrument (an otoscope) to look at the ears, throat and nasal passage. He or she will also likely listen to your child breathe with a stethoscope.
How to Prevent Ear Infections
What you need to do to prevent yourself from ear infection:
Protect yourself: remember, there is a very clear link between allergies/colds/infections and ear infections. In order to reduce your risk of ear infections, it’s vital that you boost your immune system and protect yourself from all manner of illnesses, disease, and infections. Eat foods that will enhance immunity, do exercise, and sleep well.
Take care of your health: If you are sick, take the proper medication to deal with the problem! Don’t let your allergies go unchecked, but get a prescription that will control/manage them. If you’ve got a cold, a cough, the flu, or other illnesses, visit your doctor and get the right treatment.
This will reduce your risk of secondary infections, and will restore your body to full health before the infections spread to other, sensitive places–like your ears.
Reduce Risk Factors: quit smoking immediately, and try to reduce your exposure to cigarette smoke: Avoid anything that would compromise your immune function. Take extra care of yourself as you recover from your cold, cough, flu, or allergy.
Keep Your Ears Clean: this is one of the most important ways to reduce your risk of ear infections, and one of the easiest!
Treatment for Ear Infections
Most mild ear infections clear up without intervention. Some of the following methods are effective in relieving the symptoms of a mild ear infection:
- Applying a warm cloth to the affected ear
- Taking over-the-counter pain medication such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen
- Using over-the-counter or prescription ear drops to relieve pain
- Taking over-the-counter decongestants such as pseudoephedrine
If your symptoms get worse or do not improve, you should schedule an appointment with your doctor. He or she may prescribe antibiotics if your ear infection is chronic or does not appear to be improving. If a child under the age of 2 presents with ear infection symptoms, a doctor will likely give him or her antibiotics as well. It is important to finish your entire course of antibiotics if they are prescribed.
Surgery may be an option if your ear infection is not eliminated with the usual medical treatments or if you have many ear infections over a short period of time. Most often, tubes are placed in the ears to allow fluid to drain out. In cases that involve enlarged adenoids, surgical removal of the adenoids may be necessary.
Medicine for Ear Infections
An ear infection is often caused by a virus, in which case the only relief doctors can offer is treatment of the symptoms. To ease the pain of an ear infection, your doctor may recommend a pain reliever, typically acetaminophen or ibuprofen, which also helps reduce a fever. Aspirin should be avoided in children because of the threat of Reye's syndrome. Pain can also be reduced by using gentle heat from a heating pad, but be very careful when using heating pads with children.
Sometimes, it is difficult for your doctor to tell with an otoscope alone if the ear infection is caused by a virus or bacteria, so deciding on a proper course of treatment isn't always easy. A debate over using antibiotics (bacteria-killing drugs) to treat middle ear infections arose in the 1990’s as more bacteria became resistant to antibiotics. Some doctors initially treat only the symptoms of an ear infection, without antibiotics, a response that has been supported by several studies.
Medicine for Ear Infections
An ear infection is often caused by a virus, in which case the only relief doctors can offer is treatment of the symptoms. To ease the pain of an ear infection, your doctor may recommend a pain reliever, typically acetaminophen or ibuprofen, which also helps reduce a fever. Aspirin should be avoided in children because of the threat of Reye's syndrome. Pain can also be reduced by using gentle heat from a heating pad, but be very careful when using heating pads with children.
Sometimes, it is difficult for your doctor to tell with an otoscope alone if the ear infection is caused by a virus or bacteria, so deciding on a proper course of treatment isn't always easy. A debate over using antibiotics (bacteria-killing drugs) to treat middle ear infections arose in the 1990’s as more bacteria became resistant to antibiotics. Some doctors initially treat only the symptoms of an ear infection, without antibiotics, a response that has been supported by several studies.
Ear Infections Home Remedies/Home Cure
Breast Milk: It has natural antibodies that can help speed up the healing process of any kind of ear infection. It will alleviate swelling and discomfort and can get rid of an ear infection within one or two days. This remedy works for both children and adults.
Using a dropper, put a few drops of breast milk into the affected ear.
Note: Repeat the process every few hours as needed.
Garlic
Garlic has antimicrobial properties and natural pain relieving qualities, making it highly effective in the treatment of ear infections. There are a few ways to use garlic as a home treatment.
Make garlic oil by cooking two garlic cloves in two tablespoons of sesame oil or mustard oil until it turns blackish. Strain the solution. When it is bearably hot, use two to four drops of this oil in the infected ear as ear drops.
Alternatively, you can also boil two or three fresh garlic cloves in water for five minutes, then crush them and add some salt. Put the mixture in a clean cloth and place it against the affected ear.
Consuming two to three cloves of raw garlic daily also helps speed up the healing process.
Mango Leaf Juice: Mango leaf extract is a quick and effective treatment. Crush or grind two to three soft mango leaves to extract the juice. Slightly warm the juice.
Using a dropper, put three to four drops of the juice into the infected ear, Within a few minutes, you will feel relief from the pain.
Do this remedy two to three times a day for full relief from ear infection.
These remedies can help treat minor ear infections. If there is no improvement within a couple of days, seek medical attention.
Olive Oil: One of the main causes of an ear infection is wax in the ear catching some fungal or bacterial growth leading to a blockage in the Eustachian tubes. You can easily clear the obstruction with the help of olive oil. Warm some olive oil slightly. Put a few drops of the warm oil into the infected ear.
The oil will cause the wax to soften. Remove the infected wax with cotton-tipped swabs. Be careful not to put the swab too far in the ear or you might damage the eardrum.If this is not available you can also use mustard oil.
Onion: Onion is a very common ingredient used in cooking. It has medicinal uses too, including for the treatment of an ear infection. Chop one small onion, put it in a bowl and microwave it for one to two minutes. Allow it to cool and then strain out the onion juice. Put two to three drops of the juice in the infected ear, leave it for some time and then turn your head to let it drain out of your ear.
You can also bake an onion for half an hour, cut it into halves and put one half in a thick cotton cloth. Place the cloth on the infected ear for five minutes. Wait for 10 minutes and then repeat the process.
Salt: It is probably the most readily available home remedy.
Heat up one cup of salt on a pan over low heat for a few minutes. You can also heat it in a microwave or double-boiler.
Place the hot salt on a cloth and seal the open end with rubber band (or tie a knot).
When it is bearably hot, lay down and put the cloth on the affected ear for 5 to 10 minutes.
Repeat this remedy daily as many times as needed. The heat generated from the sock will help draw out fluid from the ear and relieve swelling and pain.
As an alternative, you can use one cup of rice in the same manner described above.
Warm Water Bottle: As soon as possible, apply some heat to the infected ear. This will quickly relieve some of the pain and will also prevent micro-organism infestation.
Press a warm water bottle or heating pad against the ear.
You can also use a warm compress. Dip a clean washcloth in lukewarm water, ring out the excess water and then place the washcloth on the infected ear.
Do not apply heat to the ear for long periods of time. Start with five minutes, remove the heat for a while and then repeat the process as needed.
Complications of Ear Infections
- Brain abscess
Another rare and serious complication of otitis media is a brain abscess. A brain abscess is a pus filled swelling that develops inside the brain.
- Mastoiditis
Mastoiditis is one of the most common complications of otitis media (though still rare in general terms) and is caused when the infection spreads out of the middle ear and into the area of bone underneath the ear (the mastoids).
- Cholesteatoma
Cholesteatoma is an abnormal pocket of skin (cyst) that can sometimes develop as a complication of reoccurring or persistent middle ear infections.
- Labyrinthitis
In some cases the infection can move into the inner ear causing a delicate structure deep inside the ear, called the labyrinth, to become inflamed. This is known as labyrinthitis.
- Facial paralysis
In rare cases the swelling associated with otitis media can cause the facial nerve to become compressed.
The facial nerve is a section of nerve that runs through the skull and is used by the brain to control facial expression.
Compression of the nerve can lead to people being unable to move some, or all, of their face, which is known as facial paralysis. This complication can be frightening when it first occurs as many parents are concerned their child may have experienced a stroke or similar. But the condition usually resolves once the underlying infection has passed and rarely causes any long-term problems.
- Meningitis
A rare and serious complication of otitis media is that the infection spreads to the protective outer layer of the brain and spinal cord (the meninges) leading a serious infection known as meningitis.




