HEPATITIS B
What Is Hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B a severe form of viral hepatitis transmitted in infected blood, causing fever, debility, and jaundice. It is an inflammation of the liver.
Hepatitis B infection may be either short-lived (acute) or long lasting (chronic).
- Acute hepatitis B infection lasts less than six months. Your immune system likely can clear acute hepatitis B from your body, and you should recover completely within a few months. Most people who acquire hepatitis B as adults have an acute infection, but it can lead to chronic infection.
- Chronic hepatitis B infection lasts six months or longer. When your immune system can't fight off the acute infection, hepatitis B infection may last a lifetime, possibly leading to serious illnesses such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
The younger you are when you get hepatitis B — particularly newborns or children younger than 5 — the higher your risk the infection becoming chronic. Chronic infection may go undetected for decades until a person becomes seriously ill from liver disease.
Causes of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infection caused by the hepatitis B virus. The virus is found in the blood and bodily fluids of an infected person.
Symptoms/Signs of Hepatitis B
Dark urine/Grey-coloured poo
Diarrhea
Feeling and being sick
General aches and pains
High temperature (fever) of 38C (100.4F) or above
Loss of appetite
Tiredness
Tummy (abdominal) pain
Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
Incubation period of hepatitis b
Symptoms appear about 3 months after you have contact with the virus. But they can appear as soon as 2 months to as late as 5 months after contact.
The hepatitis B virus can be spread in the following ways:
- Have sex with an infected person without using a condom.
- Share needles (used for injecting drugs) with an infected person.
- Get a tattoo or piercing with tools that weren't sterilized.
- Share personal items like razors or toothbrushes with an infected person.
Your doctor will diagnose hepatitis B based on a physical exam and blood tests. He or she also will ask about your medical history (including possible risks for the virus, such as your job and sexual activity).
Blood tests to diagnose hepatitis B
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen TestHepatitis B Core Antigen Test
Antibody Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
Liver Function Tests
How to Prevent Hepatitis B
The hepatitis B vaccine is the best way to prevent infection. Vaccination is optional. The following groups should receive the hepatitis B vaccine:
- all infants, at the time of birth
- any children and adolescents who weren’t vaccinated at birth
- adults being treated for a sexually transmitted infection
- people living in institutional settings
- people whose work brings them into contact with blood
- HIV-positive individuals
- men who have sex with men
- people with multiple sexual partners
- injection drug users
- family members of those with hepatitis B
- individuals with chronic diseases
- people traveling to areas with high rates of hepatitis B
Treatment for acute hepatitis B infection
If your doctor determines your hepatitis B infection is acute — meaning it is short-lived and will go away on its own — you may not need treatment. Instead, your doctor might recommend rest and adequate nutrition and fluids while your body fights the infection.Treatment for chronic hepatitis B infection
If you have been diagnosed with second stage of hepatitis which is chronic hepatitis B infection, you may have treatment to reduce the risk of liver disease and prevent you from passing the infection to others. Treatments include:- Antiviral medications. Several antiviral medications — including Adefovir (Hepsera), Entecavir (Baraclude) lamivudine (Epivir) and telbivudine (Tyzeka) — can help fight the virus and slow its ability to damage your liver. Talk to your doctor about which medication might be right for you.
- Interferon alfa-2b (Intron A). This synthetic version of a substance produced by the body to fight infection is used mainly for young people with hepatitis B who don't want to undergo long-term treatment or who might want to get pregnant within a few years. It's given by injection. Side effects may include depression, difficulty breathing and chest tightness.
- Liver transplant. If your liver has been severely damaged, a liver transplant may be an option. During a liver transplant, the surgeon removes your damaged liver and replaces it with a healthy liver. In most cases transplanted livers come from deceased donors, while a small number come from living donors who donate a portion of their livers.
Hepatitis B Home Remedies/Home Cure
Home treatment can help relieve symptoms and prevent the spread of hepatitis B virus (HBV).
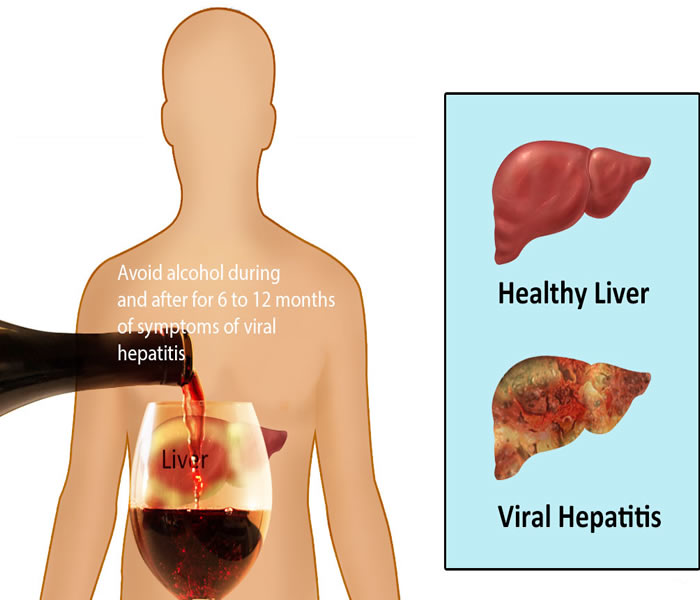
Avoid alcohol and drugs
Avoid strenuous exercise.Reduce your activity to match your energy. You don't have to stay in bed, but listen to your body. Slow down when you are tired.
Eat well make sure the food are balanced (Balanced diet)
Don't share implements. If you use IV drugs, never share needles and syringes. And don't share razor blades or toothbrushes, which may carry traces of infected blood.
Drink plenty of water to avoid dehydration.
Click here to read Natural Therapy for Hepatitis B
Complications of Hepatitis B
· Scarring of the liver (cirrhosis). The inflammation associated with a hepatitis B infection can lead to extensive liver scarring (cirrhosis), which may impair the liver's ability to function.
· Liver cancer
· Liver failure




