Asthma
What Is Asthma?
A person with asthma has fits or attacks of difficulty breathing, Listen for a hissing or wheezing sound, especially when breathing out. When he breathes in, the skin behind his collar bones and between his ribs may suck in as he tries to get air.
If the person cannot get enough air, his nails and lips may turn blue, and his neck veins may swell. Usually there is no fever.
Asthma often begins in childhood and may be a problem for life. It is not contagious, but is more common in children with relatives who have asthma. It is generally worse during certain months of the year or at night.
An asthma attack may be caused by eating or breathing things to which the person is allergic.
Asthma (AZ-ma) is a chronic (long-term) lung disease that inflames and narrows the airways.
What can leads to Asthma:
- Chest tightness
- Coughing
- Recurring periods of wheezing (a whistling sound when you breathe)
- Shortness of breath
The coughing often occurs at night or early in the morning.
Asthma affects people of all ages, but it most often starts during childhood.
Statistics
In the United States, more than 25 million people are known to have asthma. About 7 million of these people are children.
Asthma is a respiratory condition marked by spasms in the bronchi of the lungs, causing difficulty in breathing. It usually results from an allergic reaction or other forms of hypersensitivity.
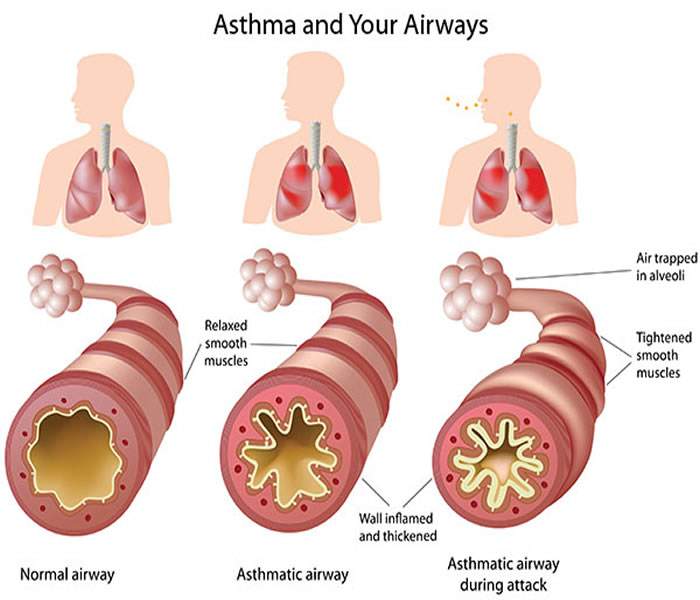
Asthma is a chronic disease involving the airways in the lungs. These airways, or bronchial tubes, allow air to come in and out of the lungs.
To understand asthma, it helps to know how the airways work. The airways are tubes that carry air into and out of your lungs. People who have asthma have inflamed airways. The inflammation makes the airways swollen and very sensitive. The airways tend to react strongly to certain inhaled substances.
When the airways react, the muscles around them tighten. This narrows the airways, causing less air to flow into the lungs. The swelling also can worsen, making the airways even narrower. Cells in the airways might make more mucus than usual. Mucus is a sticky, thick liquid that can further narrow the airways. This chain reaction can result in asthma symptoms. Symptoms can happen each time the airways are inflamed.
Causes of Asthma
Understanding the experiences or exposures that make your asthma flare-up is a key step to better managing your asthma. Making a plan to avoid or limit your exposure to your asthma triggers can eliminate asthma symptoms and put you on the right track to better control your asthma. These factors play an important role in the development of asthma.
Asthma could be triggered by these factors:
Asthma triggers are different from person to person and can include:
- Airborne substances, such as pollen, dust mites, mold spores, pet dander or particles of cockroach waste
- Certain medications, including beta blockers, aspirin, ibuprofen.
- Colds, the flu or other illnesses
- Environment. Contact with allergens, certain irritants, or exposure to viral infections as an infant or in early childhood when the immune system is not fully mature have been linked to developing asthma.
- Exercise (although people with asthma can benefit from some exercise)
- Exposure to certain chemicals and dusts in the workplace may also play a significant role in adult-onset asthma.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or Heartburn a condition in which stomach acids back up into your throat
- Genetics. Asthma tends to runs in families. Genetics play an important role in causing asthma. If your mom or dad has asthma, then you are more likely to have asthma too.
- Indoor allergens, such as pet dander, dust mites and mold
- Irritants in the air, such as smoke, chemical fumes and strong odors
- Outdoor allergens, such as pollens from grass, trees and weeds
- Respiratory Infections. As the lungs develop in infancy and early childhood, certain respiratory infections have been shown to cause inflammation and damage the lung tissue. The damage that is caused in infancy or early childhood can impact lung function long-term.
- Strong emotions and stress
- Sulfites and preservatives added to some types of foods and beverages, including shrimp, dried fruit, processed food or fruit beer and wine
- Weather conditions, such as cold air or extremely dry, wet or windy weather
Symptoms/Signs of Asthma
The most common symptom is wheezing. This is a scratchy or whistling sound when you breathe. Other symptoms include:
- Chest tightness or pain
- Chronic coughing
- Decreases or changes in lung function as measured on a peak flow meter
- Feeling very tired or weak when exercising
- Frequent cough, especially at night
- Losing your breath easily or shortness of breath
- Signs of a cold or allergies (sneezing, runny nose, cough, nasal congestion, sore throat, and headache)
- Shortness of breath
- Trouble sleeping due to coughing or wheezing
- Wheezing or coughing after exercise
The two most common lung function tests used to diagnose asthma are
- Spirometry
- Methacholine challenge tests.
Spirometry is a simple breathing test that measures how much and how fast you can blow air out of your lungs. It is often used to determine the amount of airway obstruction you have.
These Are Common Ways to Diagnose Asthma
Personal and medical history: Your doctor will ask you questions to understand your symptoms and their causes. Bring notes to help jog your memory. Be ready to answer questions about your family history, the medicines you take and your lifestyle. This includes any current physical problems. Shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing and tightness in your chest may show asthma. This also includes all previous medical conditions. A history of allergies or eczema increases your chance of asthma. A family history of asthma, allergies or eczema increases your chance of having asthma, too. Tell your doctor about any home or work exposure to environmental factors that can worsen asthma. For example, these might include pet dander, pollen, dust mites and tobacco smoke. The doctor may also ask if you get chest symptoms when you get a head cold.
Physical examination: If your doctor thinks you have asthma, they will do a physical exam. They will look at your ears, eyes, nose, throat, skin, chest and lungs. This exam may include a lung function test to detect how well you exhale air from your lungs. You may also need an X-ray of your lungs or sinuses. A physical exam then allows your doctor to review your health.
Lung function tests: To confirm asthma, your doctor may have you take one or more breathing tests known as lung function tests. These tests measure your breathing. Lung function tests are often done before and after inhaling a medication known as a bronchodilator (bron-co-DIE-a-later), which opens your airways. If your lung function improves a lot with use of a bronchodilator, you probably have asthma. Your doctor may also prescribe a trial with asthma medication to see if it helps. Common lung function tests used to diagnose asthma include:
Testing airway inflammation

It may also be useful in some cases to carry out tests to check for inflammation in your airways. This can be done in two main ways:
- A mucus sample – the doctor may take a sample of mucus (phlegm) so it can be tested for signs of inflammation in the airways
- Nitric oxide concentration – as you breathe out, the level of nitric oxide in your breath is measured using a special machine; a high level of nitric oxide can be a sign of airway inflammation
Spirometry: This is the recommended test to confirm asthma. During this test, you breathe into a mouthpiece that’s connected to a device. It is called a spirometer. The spirometer measures the amount of air you’re able to breathe in and out and its rate of flow. You will take a deep breath and then exhale forcefully.
Peak airflow: Peak expiratory flow test a small hand-held device known as a peak flow meter can be used to measure how fast you can blow air out of your lungs in one breath. This is your peak expiratory flow (PEF) and the test is usually called a peak flow test.
This test requires a bit of practice to get it right, so your GP or nurse will show you how to do it and may suggest you take the best of two or three readings.
You may be given a peak flow meter to take home and a diary to record measurements of your peak flow over a period of weeks. This is because asthma is variable and your lung function may change throughout the day.
Your diary may also have a space to record your symptoms. This helps to diagnose asthma and, once diagnosed, will help you recognize when your asthma is getting worse and aid decisions about what action to take.
To help diagnose asthma that may be related to your work (occupational asthma), your GP may ask you to take measurements of your peak expiratory flow both at work and when you are away from work. Your GP may then refer you to a specialist to confirm the diagnosis.
Trigger tests: If your other results are normal, but you’ve been experiencing signs and symptoms of asthma, your doctor may use known asthma triggers to try and provoke a mild reaction. If you don’t have asthma, you won’t react. But if you do have asthma, you likely will develop asthma symptoms.
How to Prevent Asthma
A person with asthma should avoid eating or breathing things that bring on attacks. The house or work place should be kept clean. Keep chickens and other animals outside.
Air bedding in the sunshine, Sometimes it helps to sleep outside in the open air. Drink at least 8 glasses of water each day to keep the mucus loose.
- Avoid areas where people smoke: Breathing smoke - even secondhand smoke and smoke on clothing, furniture or drapes - can trigger an asthma attack. Be sure to ask for a smoke-free hotel room when traveling.
- Avoid harsh cleaning products and chemicals.
- Avoid inhaling fumes at home and prevent exposure away from home as much as possible, Fumes from household cleaners can trigger asthma.
- Pet dander - a common asthma trigger - is often difficult to avoid entirely because for many of us, our pets are just like members of the family.
- Remove carpets and stuffed toys from bedrooms: If carpeting cannot be removed, vacuum at least twice a week with a cleaner equipped with a HEPA air filter. Ask your doctor about which cleaning products are best to use.
- Fix leaky faucets: Mold is a common asthma trigger. To reduce mold in your home, remove household plants and keep bathrooms clean and dry by opening a window or using a bathroom fan during showers or baths.
- Reduce stress: Intense emotions and worry often worsen asthma symptoms so take steps to relieve stress in your life. Make time for things you enjoy doing - and for relaxation.
- Pay attention to air quality: Extremely hot and humid weather and poor air quality can exacerbate asthma symptoms for many people. Limit outdoor activity when these conditions exist or a pollution alert has been issued.
- Exercise indoors: Physical activity is important - even for people with asthma. Reduce the risk for exercise-induced asthma attacks by working out inside on very cold or very warm days. Talk to your doctor about asthma and exercise.
- Take control of your seasonal allergies: Allergies and asthma are closely related, so talk to your doctor if you have hay fever. Use medications as directed and stay inside as much as possible when pollen counts are high.
- Make sure people around you know you have asthma: It's important for family members, friends, co-workers, teachers, and coaches to be able to recognize symptoms of an asthma attack - and know what to do if one occurs.
- Keep quick-relief asthma medicines readily available: Follow policies at your child's school to make sure he or she is allowed to carry an inhaler and any other emergency rescue medications that may be necessary. Make sure the school nurse knows your child has asthma.
- Talk to your child's teachers and coaches.
- Persons with asthma may improve when they move to where the air is cleaner.
- Use allergy-proof covers on pillows and mattresses.
- Wash bedding weekly in hot water (above 130 degrees F) to get rid of dust mites and use a dehumidifier to reduce excess moisture and help prevent mold in your home.
Chalk dust can trigger an asthma attack - so it may be helpful for your child to sit away from chalkboards in class. His or her coaches and/or physical education teacher can provide important information about asthma symptoms during exercise.
Treatment for Asthma
Asthma treatment can vary from anti-inflammatory and bronchodilator asthma inhalers to oral medications to asthma drugs delivered in an asthma nebulizer or breathing machine. Get a better understanding of how asthma medications work so you'll know which medications can prevent asthma symptoms. Also, learn about natural asthma remedies and ways to monitor your breathing at home.
The types and doses of asthma medications you need depend on your age, your symptoms, the severity of your asthma and medication side effects.
Because your asthma can change over time, work closely with your doctor to track your symptoms and adjust your asthma medications, if needed.
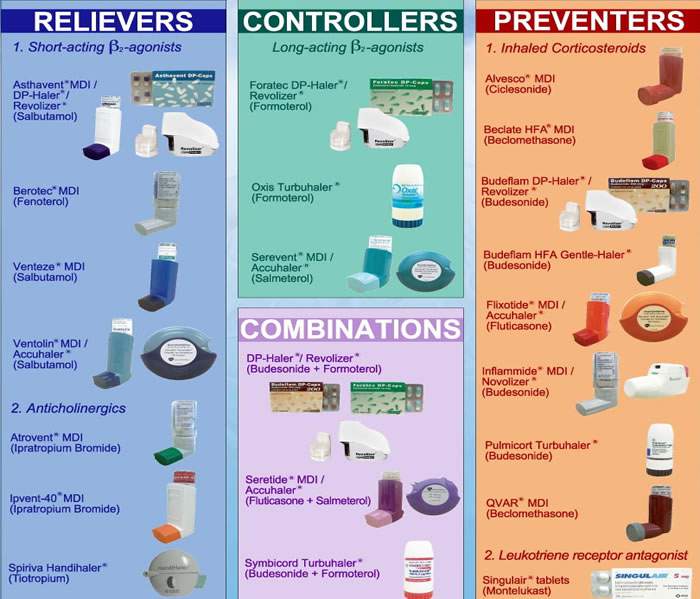
Types of asthma medications
Category |
Purpose |
Medication types |
Long-term asthma control medications |
Taken regularly to control chronic symptoms and prevent asthma attacks — the most important type of treatment for most people with asthma |
|
Quick-relief medications (rescue medications) |
Taken as needed for rapid, short-term relief of symptoms — used to prevent or treat an asthma attack |
|
Medications for allergy-induced asthma |
Taken regularly or as needed to reduce your body's sensitivity to a particular allergy-causing substance (allergen) |
Treatment
If you or a loved one has asthma, you should know about the most effective asthma treatments for short-term relief and long-term control. Understanding asthma treatments will enable you to work with your asthma doctor to confidently manage your asthma symptoms daily. When you do have an asthma attack or asthma symptoms, it's important to know when to call your doctor or asthma specialist to prevent an asthma emergency. Be sure to read all the in-depth articles that link to topics within each of the following sections. By doing so, you will gain new insight into asthma and how it's treated.
There are two types of asthma medicines: long-term controllers and quick-relievers. The difference between these can be confusing. That’s why you need to understand what each type of medicine does and how they help your asthma. It’s also important to learn how to use each medicine correctly. Always take your medicines and follow your health care provider’s instructions.
Long-Term Control Medicines
Long-term control medicines help you prevent and control asthma symptoms. You may need to take this type of medicine every day for best results. There are several kinds of long-term control medicines:
Inhaled corticosteroids prevent and reduce airway swelling. They also reduce mucus in the lungs. They are the most effective long-term control medicines available. Corticosteroids are not the same as anabolic steroids that are taken by some athletes and banned in many athletic events.
Inhaled long-acting beta agonists open the airways by relaxing the smooth muscles around the airways. If used, this type of medicine should always be taken in combination with an inhaled corticosteroid.
Combination inhaled medicines contain both an inhaled corticosteroid and a long-acting beta agonist. If you need both of these medicines, this is a convenient way to take them together.
- Omalizumab (anti-IgE) is given every 2 or 4 weeks as a shot. This medicine prevents you from reacting to allergic triggers. It does this by blocking the antibody that causes allergies. Anti-IgE is a very expensive medicine. It usually is only prescribed if other asthma medicines have not controlled your asthma.
- Leukotriene modifiers are taken in pill or liquid form. This type of medicine reduces swelling inside the airways and relaxes smooth muscles.
- Cromolyn sodium is an inhaled non-steroid medicine. It prevents airways from swelling when they come into contact with an asthma trigger.
- Theophylline comes as a tablet, capsule, solution and syrup to take by mouth. This medicine helps open the airways by relaxing the smooth muscles.
- Oral corticosteroids are taken in pill or liquid form. This medicine may be prescribed for the treatment of asthma attacks that don’t respond to other asthma medicines. They also are used as long-term therapy for some people with severe asthma. Corticosteroids are not the same as anabolic steroids taken by some athletes and banned in many athletic events.

Quick-Relief Medicines
You use quick-relief medicines to help relieve asthma symptoms when they happen. These medicines act fast to relax tight muscles around your airways. This allows the airways to open up so air can flow through them. You should take your quick-relief medicine when you have asthma symptoms. If you use this medicine more than 2 days a week, talk with your doctor about your asthma control. You may need to make changes to your treatment plan.
Short-acting beta agonists are inhaled and work quickly to relieve asthma symptoms. These medicines relax the smooth muscles around the airways and decrease swelling that blocks airflow. These medicines are the first choice for quick relief of asthma symptoms.
Anticholinergics are inhaled but act slower than the short-acting beta agonist medicines. These medicines open the airways by relaxing the smooth muscles around the airways. They also reduce mucous production.
Combination quick relief medicines contain both an anticholinergic and a short-acting beta agonist. This combination comes either as an inhaler or nebulizer for inhalation.
Asthma Home Remedies/Home Cure
Bitter Gourd: Take out the juice of bitter gourd. Add paste of basil and honey to it. Mix them well. This remedy will help in curing asthmatic attacks.
Black Tea/ Coffee: Caffeine present in coffee helps asthma. Besides, it clears your air passage and makes way for air to enter and exit easily through those passages. If you are not a coffee person, you can opt for black tea. But, make sure that you consume not more than 3 cups in a day.
Clove: Take 5-6 cloves and boil them in half a glass of water, followed by adding a spoon of honey. It is an excellent remedy in curing asthma at home and should be consumed twice in a day for beneficial results.
Ginger: Ginger has so many benefits on your heath and body. It is equally effective against asthmatic treatments. Make a juice with equal quantities of ginger, pomegranate, and honey. Consume it 2-3 times a day for effective results.
Else, take one tbsp of ginger juice. Mix it up with a tbsp of honey and two tbsp of dried fenugreek seeds. Soak it overnight and consume it every morning to detoxify your lungs.
Eucalyptus Oil: Eucalyptus essential oil can really lend a hand in keeping the asthma at bay and relieving from the existing one. Put a few drops of eucalyptus essential oil in a cup of boiling water and take its steam as it will help in opening up the nasal passages and air passages, so that air can pass through easily.
Fennel Seeds: Consume fennel seeds on a regular basis to get rid of asthmatic attacks.
Figs: Figs are another efficacious home remedy against asthma. Soak some dried figs in water, overnight. Eat them in the morning on an empty stomach. Also, drink the fig water for having an effective relief from the problem of asthma.
Fishes: Consuming fishes, such as salmon, tuna, and sardines can be really effective in treating the problem of asthma. They all make your lungs better and stronger to fight the problem of asthma and treat it quickly and effectively. However, if you cannot consume these fishes in cooked form, then you can opt for their oils.
Fruits and Lemons: Fruits, like strawberries, blueberries, papaya, and oranges have shown benefits to people, suffering from asthma. Also, lemons are rich in vitamin C and should be consumed with water and sugar at least once in a day to get cure from the disease.
Herbal Tea : Herbal tea with a dash of lime juice and crushed ginger can also serve the purpose. Herbal tea, prepared from licorice root, is also an effective treatment for asthma.
Honey: If you are looking for natural remedies for asthma, honey is the best one. You can consume a teaspoon of honey mixed in hot water at least 2-3 times a day or you can also inhale the aroma of honey. Alternatively, mix one teaspoon of honey with ½ teaspoon of cinnamon powder. Have it before sleeping.
Mustard Oil: Take some mustard oil and mix camphor in it. Massage with it all over the chest, till you get relief from the asthma. Make sure that you warm the oil before massaging with it so that your chest feels the warmth and gets relieved quickly.
Onions: Onions are known to have anti-inflammatory properties, and they are proved to be helpful in clearing air passages. So, if you are suffering from asthma, you should consume more and more of onions, be it in raw form in a salad or cooked in vegetables.
Soup: Take a radish and blend it to obtain a juice from it. Mix it with some honey and lemon juice. Consume it as it will help in clearing up your respiratory track, which will make it easier for you to breathe.
Warm Milk: Add equal quantity of olive oil and honey to a glass of warm milk. Drink this milk along with a few garlic cloves, before having breakfast. This home remedy provides natural asthma relief.
Complications of Asthma
- A collapse of part or all of the lung
- Pneumonia (infection of the lungs)
- Respiratory failure, where the levels of oxygen in the blood become dangerously low, or the levels of carbon dioxide become dangerously high.
- Fatigue
- Psychological problems including stress, anxiety and depression.
- Underperformance or absence from work
- Death: Severe asthma attacks constrict the airway. This can lead to complete respiratory failure and death if not treated immediately. The AAFA estimates that 9 Americans die from asthma every day. There are more than 4,000 asthma-related deaths a year in America. However, the AAFA also indicates that many of these deaths could be prevented with proper symptom and emergency care.




