Dengue (Breakbone Fever)
What Is Dengue (Breakbone Fever)?
Dengue (Breakbone Fever) is a mosquito-borne disease caused by a virus.
This illness is sometimes confused with malaria. It is caused by a virus that is spread by mosquitos. In recent years it has become much more common in many countries. It often occurs in epidemics (many persons get it at the same time), usually during the hot, rainy season. A person can get dengue more than once.
Dengue fever may occur in people of all ages who are exposed to infected mosquitoes
Dengue fever can be commonly found in urban parts of subtropical and tropical areas, like The Pacific Islands, The Caribbean (except Cuba and the Cayman Islands), Mexico, Africa, Central and South America.
Causes of Dengue (Breakbone Fever)
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus.
Symptoms/Signs of Dengue (Breakbone Fever)
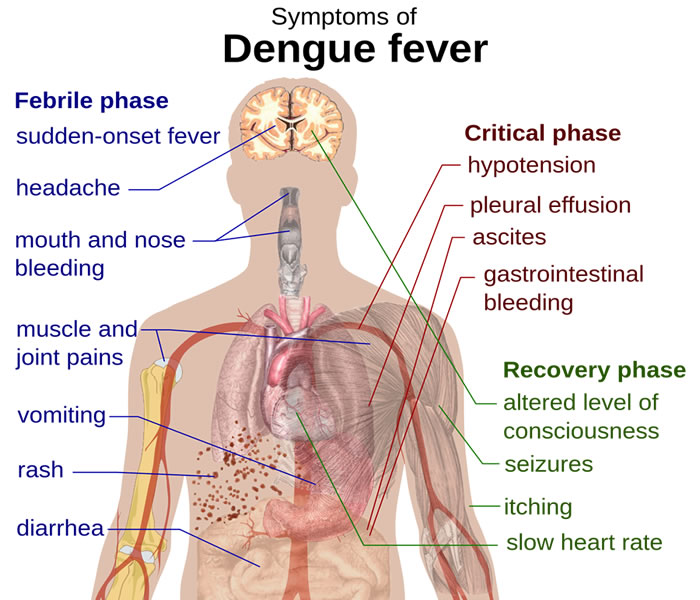
- Aching muscles and joints
- Body rash that can disappear and then reappear
- Sudden high fever
- Intense headache
- Loss of appetite.
- Pain behind the eyes
- Feeling very ill, weak and miserable.
- On and off fever.
- Severe body aches, headache, sore throat.
- Then illness returns for one or two days, often with a rash that begins on hands and feet
- Vomiting and feeling nauseous.
When a patient exhibits the typical clinical symptoms listed above, your doctor will ask you to conduct a blood test, Dengue fever can be difficult to diagnose because its symptoms overlap with those of many other viral illnesses, such as West Nile virus and chikungunya fever.
How to Prevent Dengue (Breakbone Fever)
There is no vaccine to prevent dengue fever. The best way to prevent the disease is to prevent bites by infected mosquitoes, particularly if you are living in or traveling to a tropical area. This involves protecting yourself and making efforts to eradicate the mosquito population down.
Treatment for Dengue (Breakbone Fever)
Because dengue fever is caused by a virus, there are no specific antibiotics to treat it.
But the illness goes away by itself in a few days.
The treatment is concerned with relief of the symptoms and signs rest, lots of liquids such as rehydration drink, fruit juice, or milk, acetaminophen (but not aspirin or ibuprofen) for fever and pain.
Dengue (Breakbone Fever) Home Remedies/Home Cure
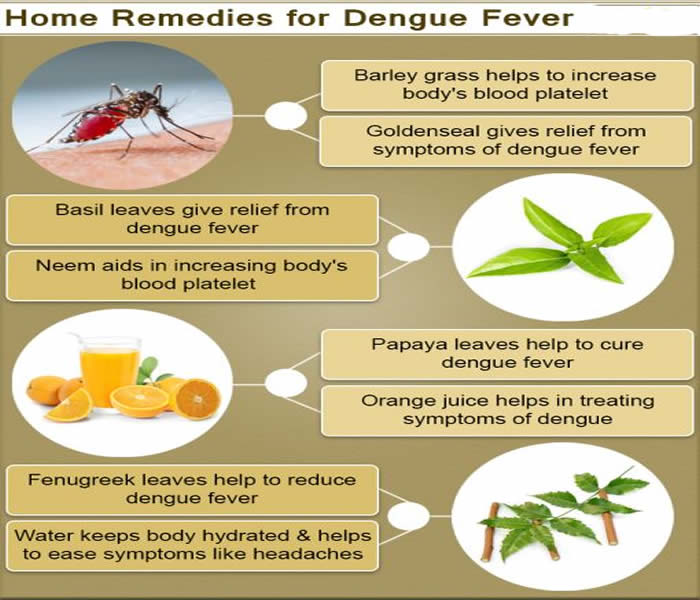
- Water: This may seem like common sense, but due to the excessive sweating, bodily exertion, and the internal toll that dengue fever takes on the body, extreme dehydration is common. Drink as much water as possible to keep the body hydrated, which will also help to ease symptoms like headaches and muscle cramps, both of which are exacerbated by dehydration. Furthermore, water will help to flush the body and eliminate excess toxins that can complicate the viral impact of the pathogen.
- Neem Leaves: Neem leaves are commonly prescribed for a variety of ailments, and dengue fever is no exception. Steeping neem leaves and then drinking the subsequent brew has been shown to increase both blood platelet count and white blood cell count, two of the most dangerous side effects of the virus. Properly brewed neem leaves can improve the immune system and return your strength much faster than many other home remedies.
- Papaya Leaves: Although the exact pathway is unclear, papaya leaves are widely known as being a natural cure for dengue fever. The complex mix of nutrients and organic compounds in papayas can cause a rise in your platelet count, the high levels of vitamin C help stimulate the immune system, and the antioxidants help to reduce oxidative stress and eliminate excess toxins in the blood. The leaves can be crushed and then strained with a cloth to drink the pure juice.
- Orange Juice: The rich mixture of antioxidants and vitamins found in orange juice make it ideal for treating the secondary symptoms of dengue fever and eliminating the virus. Orange juice helps to promote antibodies of the immune system, increase urination and the release of toxins, and stimulates cellular repair due to vitamin Cs crucial role in the creation of collagen.
- Bleeding from gums and nose
- Failure in the circulatory system
- Damage to blood and lymph vessels
- Leakage of blood plasma
- Liver enlargement
- Low levels of blood platelets.




