Thyroid Goiter
What Is Thyroid Goiter?
Goiter is a swelling of the neck resulting from enlargement of the thyroid gland.
A goiter is an enlarged thyroid gland. The thyroid is the gland in front of the neck.
Goiter is the name given to a neck swelling produced by an abnormally enlarged thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is situated in front of the windpipe and is responsible for producing and secreting hormones that regulate growth and metabolism.
Goiters can be any one of several types of growths in the thyroid gland, located at the base of the front side of the neck just below the Adam's apple.
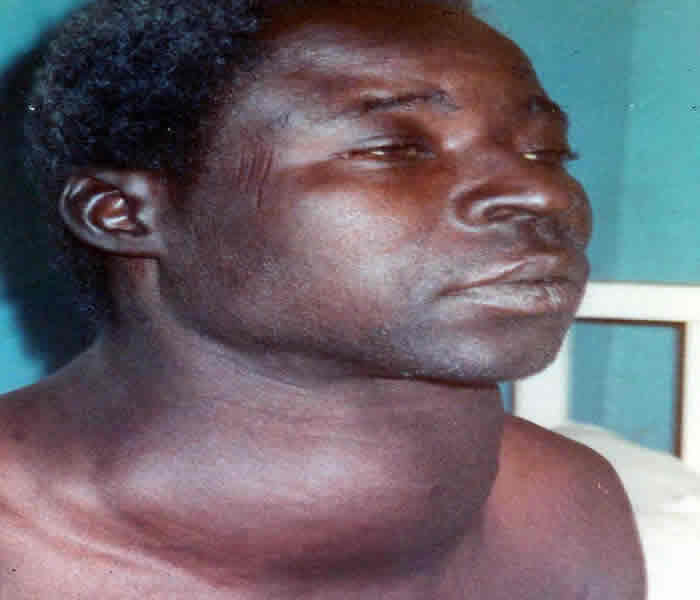
Causes of Thyroid Goiter
The major cause of goiter is Iodine deficiency. Goiter is rare in economically developed countries that add iodine to salt.
Goiters can also occur when the thyroid gland produces either too much thyroid hormone or not enough hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism respectively. The problem may arise when the pituitary gland stimulates thyroid growth to boost production of the hormone. Enlargement could also occur with normal production of thyroid hormone, such as a nontoxic multinodular gland.
As for developed countries the main cause of goiter is autoimmune disease. Women over the age of 40 are at greater risk of goiter.
Hypothyroidism is the result of an underactive thyroid gland, and this causes goiter.
Hypothyroidism is also a cause of goiter - from an overactive thyroid gland, which produces too much thyroid hormone.
Rarely conditions that causes goiter are:
- Hormonal changes - pregnancy, puberty and the menopause can affect thyroid function
- Nodules - benign lumps, single or multiple
- Thyroiditis - inflammation caused by infection, for example
- Lithium - the psychiatric drug can interfere with thyroid function
- Overconsumption of iodine - Excess iodine can cause goiter
- Smoking - The content of tobacco called thiocyanate interferes with iodine absorption
- Radiation therapy - most especially if it is in the neck.
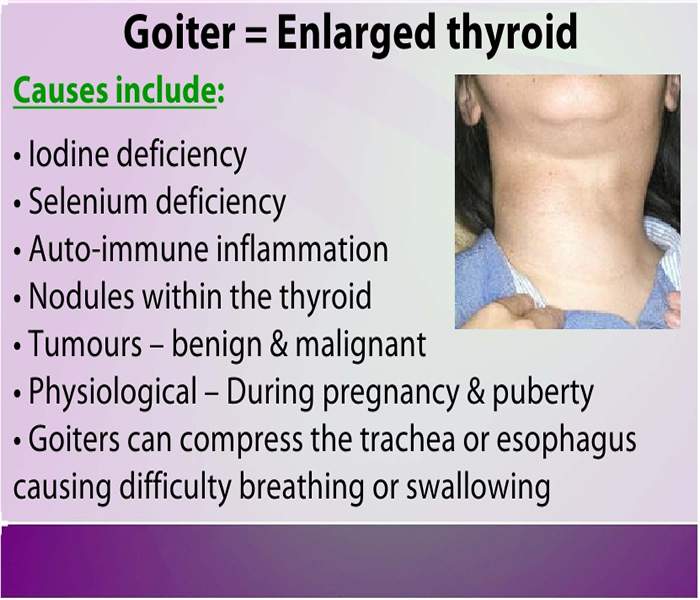
Symptoms/Signs of Thyroid Goiter
- Difficulty breathing
- Difficulty concentrating
- Difficulty swallowing(dysphagia)
- Dry cough and hoarseness
- Dry skin, nails and hair
- Drowsiness
- Fatigue
- Increased menstrual flow
- Throat tightness
- Visible swelling at the base of your neck
How to diagnose Thyroid Goiter
The most important part of diagnose goiter is the doctor's examination. Commonly the doctor will diagnose a goiter using some or all of the following techniques:
- Blood test
- Feeling the thyroid
- Thyroid scan
- Ultrasound
Feeling the Thyroid
By feeling the thyroid, the doctor can estimate the size of the gland, tell whether it is growing or not, and tell if it has any lumps in it that might be suspicious for cancer.
Blood Test
Measurement of the levels of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and T4 in the blood stream are important because they help the doctor determine whether or not the goiter is making a normal amount of thyroid hormone. If the gland has a lump in it, the doctor may order a thyroid scan or an ultrasound to see if there are any masses in the thyroid that might be suspicious for a thyroid cancer.
Thyroid Scan
A thyroid scan is performed by having the patient take oral capsules that contain a harmless radioactive tracer (which is a tiny quantity of radioactive iodine). After four, six, or twenty-four hours (depending on the institution) a detector is placed over the thyroid gland. The amount of radioactive iodine that wound up in the thyroid gland is measured and a picture is taken of the distribution of radioactive iodine in the thyroid. In a normal thyroid gland, radioactive iodine is taken up to the same degree throughout the entire gland. If there is an area of the thyroid that does not take up radioactive iodine well, then it must be further investigated. The majority of these "cold" areas on a thyroid scan are benign, but about 5-10% of them are thyroid cancers. Under such circumstances an ultrasound might be ordered.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a way of taking a picture of the inside of the thyroid. Ultrasound bounces sound waves off the thyroid and makes a picture out of the returning echoes. If the ultrasound shows a large mass that is suspicious for cancer, then the ultrasonographer can use the ultrasound to guide a needle into the mass to perform a fine needle aspiration biopsy. If there are no large lumps in the thyroid gland that are suspicious for cancer, then no biopsy needs to be done. BY netwellness
How to Prevent Thyroid Goiter
Preventing simple goiter is as easy as a small change in diet. Iodine is necessary for producing thyroid hormones. Some patients do not eat enough iodine, so it causes the thyroid to work overtime to produce thyroid hormones. Using iodized table salt can prevent simple goiter.
Diet to prevent Goiter
- Fresh fruit juice for five days. During this period take a glass of juice of orange or other juicy fruit diluted with water every two hours from 8 a.m. To 8 p.m. And cleanse the bowels daily with warm water enema.
- A diet of fresh juicy fruit for further five days, with three meals a (jay at 'five-hourly intervals.
- Thereafter, adopt a well-balanced diet on the following lines:-
1. Early in the morning:
- A glass of lukewarm water
- A half a freshly squeezed lime
- A teaspoon of honey
2. Breakfast:
- Fresh fruits
- A glass of milk
- Sweetened with honey
- Seeds or nuts
3. Lunch:
- A bowl of freshly prepared steamed vegetables
- 2/3 whole wheat
- A glass of buttermilk
4. Mid-afternoon
- A glass of fruit
- Vegetable juice
- A large bowl of fresh green vegetable salad
- Lime juice
- Sprouted green gram beans
Things and Diet to avoid:
- Alcoholic beverages
- Avoid refined foods
- Condiments pickles
- Coffee
- Products made with them
- Fried foods
- Flesh foods
- Smoking
- Sugar
- Tea
- White flour
Best Fruits and vegetables for the condition:
- Asparagus
- Cabbage
- Carrots
- Garlic
- Onion
- Oats
- Pineapple
- Strawberries
- Tomatoes
- Whole rice
These also important:
1. Plenty of rest and adequate sleep
2. Fresh air, breathing and other light exercises
3. Ice bag over throat and heart region.
Treatment for Thyroid Goiter
A goiter may not need treatment if it is small and not growing. Treatment would be necessary for the following reasons:
- Size inhibits function of parts of the neck
- Growth is fast enough to cause problems in the near future
- Unsightly appearance
If the thyroid were large enough to press on the swallowing tube, breathing tube, or nerve to the voice box, this pressure might cause difficulty swallowing, shortness of breath, or hoarseness in the voice. It might be important to treat a goiter that was growing in order to keep it from eventually pressing on these important structures and causing symptoms. Finally, if the goiter is large enough to be unsightly, the patient might want it treated for cosmetic reasons.
The best treatment for a goiter is a subtotal thyroidectomy. This is an operation in which most of the thyroid gland is removed. There are some research studies suggesting that putting a patient on a thyroid hormone pill everyday may help to shrink goiters or keep them from growing. However, there are other studies suggesting that this may not work. There are also studies suggesting that even a mild overdose of thyroid hormone, if taken for many years, can result in osteoporosis and may put older individuals at risk for abnormal heart rhythms.
Thyroid Goiter Home Remedies/Home Cure
Garlic
According to researchers, garlic decreases swelling of your neck caused by enlarged thyroid gland. He recommends eating garlic at least thrice a week. Many other researchers have also supported garlic as beneficial in treating thyroid problems. There are many plant chemicals that act as antioxidants and in maintaining body cell functions. Many studies have shown that garlic extracts, especially the aged garlic extract, increase production of glutathione. Glutathione is a molecule which is important in maintaining a healthy status of thyroid hormone. So, include garlic in your diet. Here are some ways that you can imply for eating garlic for overall health.
How to use it
- Chew 3-4 raw garlic cloves in the morning.
- Add raw garlic with tomatoes, onion, olive oil to make your own salsa.
- Add minced raw garlic with lemon juice, and parsley to make salad dressing.
- Sprinkle raw minced garlic on buttered toast.
- Add garlic to mashed avocados to make a delicious dip
- Add minced garlic to your sauces.
- Use garlic in mashed potatoes.
- Make tea with garlic, honey and lemon
Green Tea
Green tea is yet another remedy that can prevent and cure your goiter. Due to its stimulating and energy boosting properties, green tea enhances the functioning of thyroid gland. It is also high in natural fluoride and thus supports thyroid. Its antioxidants fight free radicals that are known to promote the growth of goitres and even tumors. Have three cups of green tea everyday.
Ingredient
Green tea leaves- 1 tsp (may also use green tea bags)
Hot water- 1 cup
Honey (optional)- 1-2 tsp
How to use it
- Put the tea leaves in a pot
- Pour the hot water over it.
- Let it steep for 2-5 minutes.
- Strain
- Add honey if using and mix well.
- Have this green tea three times a day.
Iodine Rich Diet
Deficiency of iodine is one of the major causes of goiter. You need to take a nutrient rich diet with adequate iodine. Now what is adequate amount of iodine? It is not too much, just 150 micrograms for adults; 50 micrograms for kids within the age of 1 to 6; and 90 micrograms for children between 7 to 12 years of age. Pregnant women, however, need a little more iodine, 200 micrograms to be precise. So, include iodine rich foods in your daily diet to cure as well as prevent goiter and hypothyroidism.
List of iodine rich foods
- Iodized salt
- Baked potato with peel
- Cabbage
- Cod
- Cranberries
- Eggs
- Milk
- Shrimp
- Navy beans
- Plain yogurt
- Seafood
- Tuna
- Turkey
Selenium Rich Foods
While iodine deficiency can cause goiter., deficiency of selenium can cause ‘weighty’ thyroid which is heavy too. When you provide selenium to your body, it synthesizes it. During the process of synthesis, selenium is converted into one of many types of selenoproteins. There are eleven selenoproteins that get involved with thyroid and production of thyroid hormone. Many researches have found that selenium protects against goiter. So have selenium rich foods to keep it at a satisfactory level in your body.
List of selenium rich foods
- Brazil nuts
- Clams
- Crab
- Grains- wheat germ, barley, brown rice, oats
- Eggs
- Fish- tuna, halibut, sardines, flounder, salmon
- Kidney
- Liver
- Mussels
- Meat- Beef, lamb, pork
- Mushrooms
- Onions
- Poultry- Chicken, turkey
- Sunflower Seeds
- Shellfish- oysters
- Shrimp
- Scallops
Sorrel Leaves
Sorrel leaves, also called spinach dock, can not only be used for making soups, salads and sauces but also to treat goiter. The way of using these leaves is similar to that of the other two remedies we have discussed above- in paste form.
Ingredient
Olive oil- 2 tbsp
Sorrel leaves- a handful of them
How to use it
- Add olive oil to this paste and mix well.
- Apply this paste on your neck.
- Crush the sorrel leaves to make a paste.
- Leave for about 15-20 minutes.
- Wash off with water and pat dry.
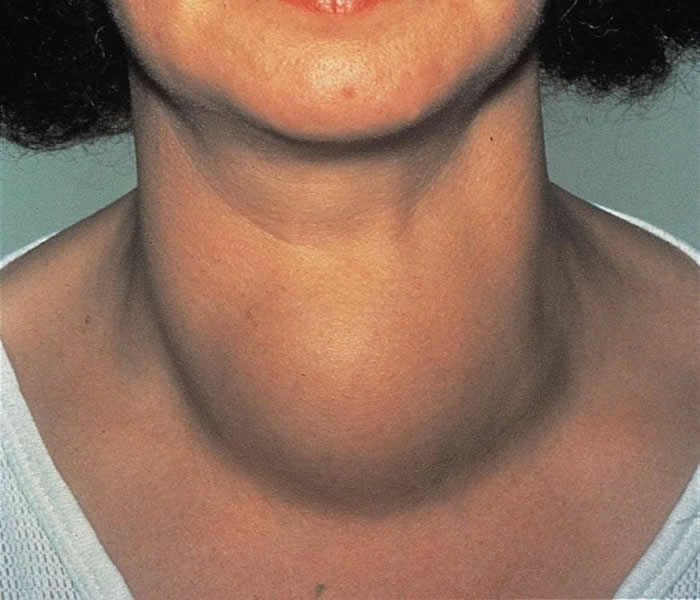
Complications of Thyroid Goiter
In severe cases, difficulty breathing (possibly with a high-pitch sound)
Large goiters can make it hard to breathe
- Cough
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Hoarseness
Goiters can also result to conditions such as:
- Hypothyroidism
- Hyperthyroidism
Complications of Thyroid Surgery
Bleeding in the neck — occurs only in about 1/300 thyroid operations. The amount of bleeding is usually small, but even small amounts of blood can compress the windpipe and cause difficulty breathing. In that case, it may be necessary to perform an urgent operation to drain the blood and relieve the pressure. Needing a blood transfusion is very rare for thyroid surgery.
Seroma — is a fluid collection under the incision which feels like fullness or swelling. When minor, this gets better in a few days or weeks. If it is large, it may be drained by the surgeon.
Infection — occurs in about 1/2000 thyroid operations, and the routine use of antibiotics to prevent infection is not necessary. In general, the neck is a clean area that usually does not get infected. However, if a postoperative infection does develop, drainage of the infected fluid and/or antibiotics may be necessary.
Temporary voice changes, such as mild hoarseness, voice tiring, and weakness are more common and can happen in 5 to 10% of patients. The temporary problem usually occurs because one or more of the nerves are irritated either by moving them out of the way during the operation or because of the inflammation that happens after the surgery. Although the voice usually improves in the first few weeks after surgery, it can last up to 6 months.
Voice change — is a known complication after thyroid surgery. There are two sets of nerves near the thyroid gland that help control the voice. These are the recurrent laryngeal nerve and the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. Damage to a recurrent laryngeal nerve can cause you "to lose your voice". The chance that one of the recurrent laryngeal nerves will be permanently damaged is about 1%. A more subtle change in vocal function may be noticeable if you are a professional voice singer or public speaker.




