Tuberculosis
What Is Tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis, also referred to as TB, is a highly contagious respiratory infection caused by the bacteria known as ‘mycobacterium tuberculosis. (TB) is a bacterial infection spread through inhaling tiny droplets from the coughs or sneezes of an infected person.
It is a serious condition, but can be cured with proper treatment. TB mainly affects the lungs. However, it can affect any part of the body, including the glands, bones and nervous system.
According to the statistics TB is an infectious disease that usually affects the lungs. It is the second greatest killer due to a single infectious agent worldwide.
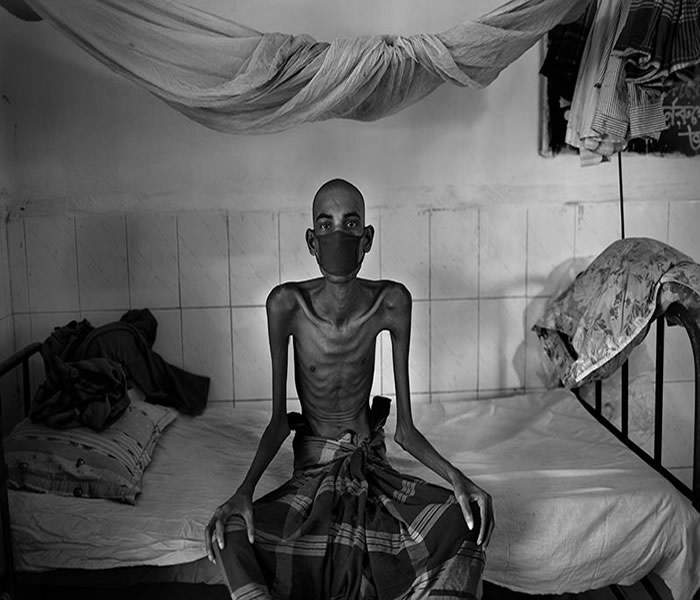
TB is highly contagious, there are high chances of catching TB from someone whom you see and have physical contact with or live and work with. When most people with active TB start to receive appropriate treatment for at least two weeks the probability of contacting TB from them is very slim.
Facts on tuberculosis
TB is a deadly disease but it is curable and preventable.
In 2014 not less than 1.5 million people died of TB of which one quarter of a million of them were living with HIV
About 95% of death happened in developing country 1n 2014 were caused by TB.
Majority of TB victims are women within age of 15 and 50years.The most common diagnostic test for tuberculosis is a skin test.
Tobacco use has been found to increase the risk of developing active TB with more than 20% of TB cases worldwide attributable to smoking.
Causes of Tuberculosis
All cases of TB are passed from person to person through body fluid/droplets. When someone with TB infection in their lungs coughs, sneezes, spits, laughs or talks the tiny droplets of saliva or mucus are expelled into the air, which can be inhaled by another person.
Symptoms/Signs of Tuberculosis
A person with TB infection will have no symptoms. A person with active TB disease may have any or all of the following symptoms:
- Constant fatigue
- Coughing up blood
- Coughing that lasts three or more weeks
- Chest pain, or pain with breathing or coughing
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
How to diagnose Tuberculosis
There are several TB tests available to diagnosis
- Chest X-ray
- Culturing bacteria to test for TB
- Fluorescent microscopy
- Serological tests (TB blood tests)
- Sputum smear microscopy
- TB drug susceptibility tests
- The TB skin test (TST)
The most common diagnostic test for tuberculosis is a skin test.
How to Prevent Tuberculosis
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that one-third of the world's population is infected with the bacteria that cause TB.
To avoid getting an active TB infection there are many things you need to know:
- Avoid any contact with tiny druplet of saliva or mucus that expelled from TB patients.
- Cut down on alcohol consumption and avoid smoking or taking drugs.
- not use any cloth or handcarchief of TB patient unless he has taken proper treatment for at least two weeks.
- Do not share house utesils such as cup, spoon and plate with anyone that has active infection.
- Do not spend long periods of time in stuffy, enclosed rooms with anyone who has active TB until that person has been treated for at least 2 weeks.
- Eat a healthy, balanced diet with plenty of fruit, vegetables, whole grains and lean meat. Avoid fatty, sugary and processed foods.
- Get the BCG vaccination to prevent TB. Use protective measures, such as face masks, if you work in a facility that cares for people who have untreated TB.
- If you live with someone who has active TB, help and encourage the person to follow treatment instructions.
Treatment for Tuberculosis
TB disease can be treated by taking several drugs for 6 to 9 months. There are 10 drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating TB. Of the approved drugs, the first-line anti-TB agents that form the core of treatment regimens include:
- isoniazid (INH)
- rifampin (RIF)
- ethambutol (EMB)
- pyrazinamide (PZA)
Treatment takes that long because the disease organisms grow very slowly and, unfortunately, also die very slowly.
Who Is at Risk for TB Disease?
Everybody can contact TB but some people are most at risk:
- An health-care workers
- HIV patients,(they have an immune system problem)
- Someone who have lived in a crowded conditions,such as prisons
- People who have severe kidney disease
- People who have certain cancers
- Someone who has taken some kind of cancer treatment, such as chemotherapy
- People that are using some hard drugs to treat rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease and psoriasis
- Malnutrition
- Smokers
Tuberculosis Home Remedies/Home Cure
1. Garlic
Garlic is rich in sulfuric acid that destroys the germs causing TB. It also contains allicin and ajoene, which have been found to inhibit bacterial growth. Plus, its antibacterial properties and immune-boosting effect are highly beneficial for a TB patient. Garlic can be eaten raw or cooked.
Mix together one-half teaspoon of chopped garlic, one cup of milk and four cups of water. Boil it until it is reduced to one–fourth of the volume. Drink the mixture three times daily.
Add 10 drops of garlic juice to a glass of hot milk and drink it before going to bed. Do not drink water afterwards, as it may diminish the beneficial effects.
Dice 10 cloves of garlic and boil them in one cup of milk. Eat the boiled pieces of garlic and then drink the milk. Do this daily for a few months.
2. Bananas
Bananas are an excellent source of nutrients and calcium that can help boost a TB patient’s immune system. They also can help alleviate the cough and fever.
Take a ripe banana, mash it and mix in one cup coconut water, one-half cup yogurt, and one teaspoon honey. Consume it twice daily.
Make raw banana juice and drink one glass of it daily.
You can also drink the juice of the banana plant stem to relieve symptoms like chronic cough, excess phlegm, excessive perspiration at night with a high fever and so on. Slowly sip one to two cups of banana stem juice every two hours until symptoms subside.
3. Drumstick
Drumstick has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties that can help eliminate the TB-causing bacteria from the lungs and reduce inflammation resulting from the infection and constant coughing. Plus, drumstick pods and leaves are a good source of carotene, calcium, phosphorus and vitamin C.
Boil a handful of drumstick leaves in one cup of water for five minutes.
Allow it to cool and add salt, pepper and lime juice.
Drink this daily in the morning on an empty stomach.
Also boiled drumsticks can be consumed daily to get relief from the infection.
4. Indian Gooseberry
Indian gooseberry, also known as amla, has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. The various nutrients in Indian gooseberry provide energy and enhance the body’s capacity to function properly.
De-seed three or four Indian gooseberries. Extract the juice with the help of a juicer.
Add one tablespoon of honey and mix it well.
Drink this every morning on an empty stomach.
Raw Indian gooseberry or its powder can also be consumed.
5. Oranges
Oranges have many essential minerals and compounds. Orange juice has a saline action in the lungs, which eases expectorations and protects the body from secondary infections. It can boost the immune system as well.
Add a pinch of salt and one tablespoon of honey to a glass of freshly squeezed orange juice. Mix it thoroughly.
Drink this twice daily, one glass in the morning and another in the evening.
6. Custard Apple
The rejuvenating properties in custard apple can also help in the treatment of tuberculosis. Usually the pulp of custard apple is used.
Boil the pulp of two custard apples and 25 seedless raisins in one and a half cups of water until one-third of the water is left.
Strain the mixture and add two teaspoons of powdered sugar and one-quarter teaspoon each of cardamom and cinnamon. Allow it to cool.
Drink this twice daily.
By top10homeremedies.com
Complications of Tuberculosis
Although some people may develop no complications, others range from mild to severe complications, including death. Some of the more severe complications include lung function damage, bone pain (spine, ribs, and joints), meningitis, kidney and/or liver malfunction, cardiac tamponade, and visual disturbances.
Click here to read Natural Therapy for Tuberculosis




