Unconsciousness or Loss of Consciousness
What Is Unconsciousness or loss of consciousness?
Unconsciousness is when a person suddenly becomes unable to respond to stimuli and appears to be asleep. It is a partial or complete loss of awareness of oneself and ones surroundings.
A person may be unconscious for a few seconds (fainting) or for longer periods of time.
People who become unconscious don’t respond to loud sounds or shaking. They may even stop breathing or their pulse may become faint.
What Causes Unconsciousness?
Common causes of unconsciousness include:
• Alcohol (drunkenness)
• A hit on the head or chest (getting knocked out)
• Shock
• Seizures
• Poisoning
• Fainting (from fright, weakness, low blood sugar, etc.)
• Heat stroke
• Stroke
• Heart attack
• A car accident
• Severe blood loss
• A drug overdose
• Hyperventilating
• Dehydration
Signs that a Person May Become Unconscious
Symptoms that may indicate that unconsciousness is about to occur include:
- Sudden inability to respond
- Slurred speech
- A rapid heartbeat
- Confusion
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Very pale skin
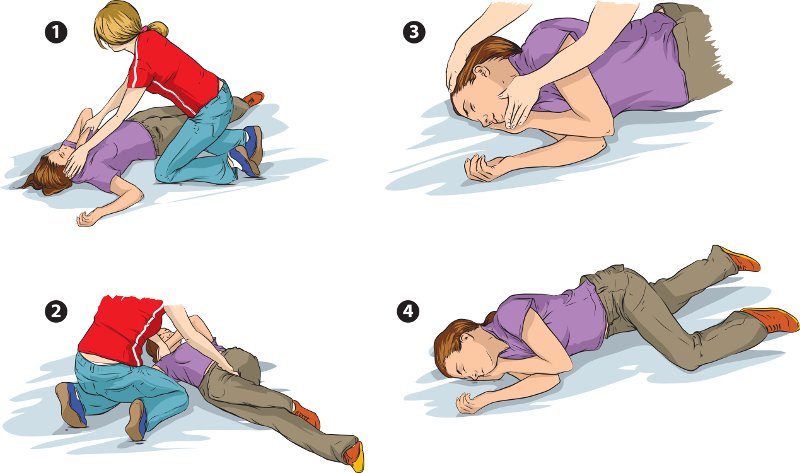
How to position an unconscious person:
If there is any chance that the unconscious person is badly injured:
- It is best not to move him until he becomes conscious. If you have to move him, do so with great care, because if his neck or back is broken, any change of position may cause greater injury.
- Look for wounds or broken bones, but move the person as little as possible. Do not bend his back or neck.
- Never give anything by mouth to a person who is unconscious.
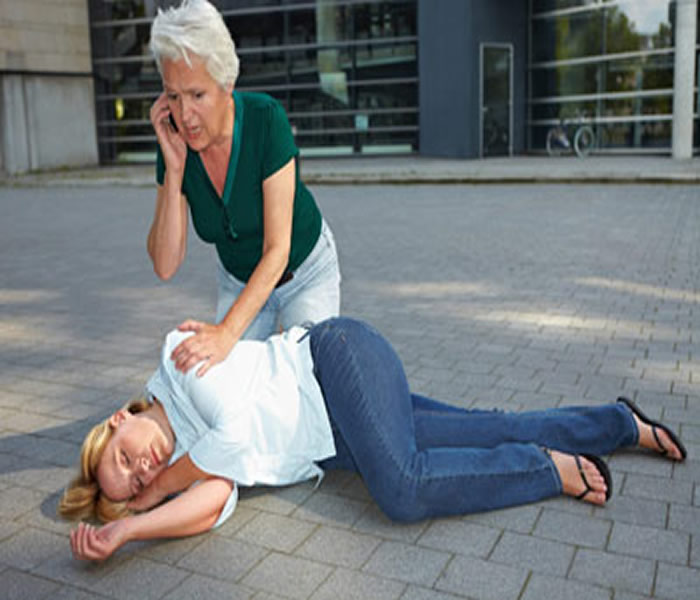
Administering First Aid
If a person is unconscious and you do not know why, immediately check each of
the following:
1. Is he breathing well? If not, tilt his head way back and pull the jaw and tongue
forward. If something is stuck in his throat, pull it out. If he is not breathing, use
mouth-to-mouth breathing at once
2. Is he losing a lot of blood? If so, control the bleeding.
3. Is he in shock (moist, pale skin; weak, rapid pulse)? If so, lay him with his head
lower than his feet and loosen his clothing.
4. Could it be heat stroke (no sweat, high fever, hot, red skin)? If so, shade him
from the sun, keep his head higher than his feet, and soak him with cold water (ice
water if possible) and fan him
Check again to see if the person is breathing, coughing, or moving. These are signs of positive circulation. If these signs are absent, perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) until emergency personnel arrive.
CPR Instructions
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a way to treat someone when they stop breathing or their heart stops beating.
Before beginning CPR, ask loudly, “Are you okay?” If the person doesn’t respond, begin CPR.
Lay the person on their back on a firm surface.
Kneel next to the person’s neck and shoulders.
Place the heel of your hand over the center of the person’s chest. Put your other hand directly over the first one and interlace your fingers. Make sure that your elbows are straight and move your shoulders up above your hands.
Using your upper body weight, push straight down on the person’s chest at least 1.5 inches for children, or 2 inches for adults. Then release the pressure. Repeat this procedure again up to 100 times per minute. These are called chest compressions.
How Is Unconsciousness Treated?
If unconsciousness is due to low blood pressure, a doctor will administer medication by injection to increase blood pressure. If low blood sugar level is the cause, they may need something sweet to eat or a glucose injection.
Medical staff should treat any injuries that caused the person to become unconscious.
Complications of Unconsciousness
Potential complications of being unconscious for a long period of time include:
- Coma
- Brain damage
- Broken or fractured ribs from the chest compression during CPR
- Choking can also occur during unconsciousness. Food or liquid may have blocked your airway. This is particularly dangerous and could lead to death if it isn’t remedied.

What Is the Long-Term Outlook?
Your outlook will depend on what caused you to lose consciousness. However, the sooner you receive emergency treatment, the better your outlook will be.




